Smart Grid Market Overview
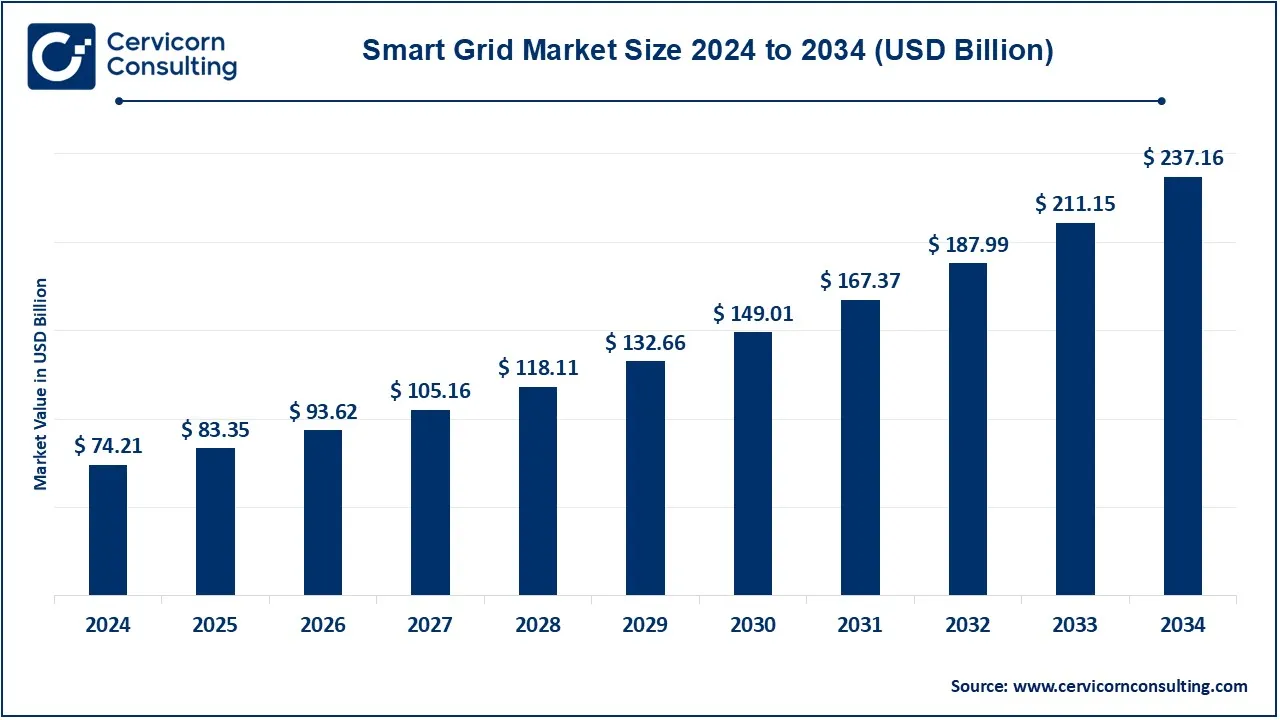
The global smart grid market is experiencing rapid expansion, propelled by the growing need for improved energy efficiency, reliability, and seamless integration of renewable power sources. In 2024, the market stood at USD 74.21 billion and is forecasted to reach USD 237.16 billion by 2034, registering a CAGR of 17.2% throughout the projection period. Smart grids merge advanced IT systems, automation, and digital communication technologies with traditional power grids, enabling smarter electricity generation, transmission, and consumption management.
The ecosystem includes multiple components such as smart meters, distribution automation, grid management software, and next-generation communication frameworks. Rising electricity demand, aging grid infrastructure, and the ongoing shift toward sustainable energy solutions are accelerating global adoption.
👉 Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2491
Key Market Trends
The evolution of the smart grid market is being shaped by several technological, regulatory, and consumer-focused trends:
1. IoT and AI Integration in Grid Operations
Utilities are increasingly embracing AI- and IoT-powered sensors to track energy flows, forecast demand, and detect faults in real time. Predictive maintenance enabled by AI is proving effective in minimizing downtime and reducing operational expenses.
2. Expanding Use of Smart Meters
Smart meters provide real-time energy consumption data and automate billing processes. Governments in countries like the United States and Germany are promoting widespread deployment, empowering consumers to better control energy usage and lower costs.
3. Renewable Energy-Driven Regulations
Policies encouraging the adoption of solar and wind energy are pushing utilities to deploy intelligent grids capable of handling intermittent power supply. Regulatory incentives are serving as a key catalyst for this transformation.
4. Electric Vehicle (EV) and Grid Synergy
The surge in electric vehicle adoption is boosting demand for vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies. Smart grids help balance loads by enabling bidirectional energy transfer between EVs and the grid, improving overall energy resilience.
5. Cybersecurity and Resilience Measures
With grids becoming increasingly digital, cybersecurity has emerged as a top priority. Utilities are investing in secure, resilient infrastructures to safeguard against cyber threats and ensure uninterrupted energy supply.
Market Drivers
Several factors are fueling market growth:
-
Rising Energy Consumption: Global power demand is set to grow significantly by 2030, creating the need for more efficient and reliable grid systems.
-
Government Support: Initiatives such as the US Smart Grid Investment Grant (SGIG) and EU smart grid directives are fostering large-scale implementation.
-
Advancements in Technology: Breakthroughs in IoT, AI, machine learning, and communication protocols are enhancing efficiency and grid stability.
-
Consumer Demand for Efficiency: Growing public awareness around sustainability, cost savings, and energy efficiency is spurring demand for smart meters and home energy solutions.
Notably, global smart meter installations are forecasted to surpass 1.1 billion units by 2030, underscoring robust growth prospects.
Impact of Trends and Drivers
The influence of these factors varies across segments:
-
By Component: Smart meters and grid management software are expected to dominate adoption, largely due to compliance mandates and consumer-driven efficiency needs.
-
By Region: North America and Europe lead adoption, supported by policy frameworks and advanced grid infrastructures, while Asia-Pacific is gaining ground with rapid urbanization and surging energy demand.
-
By Application: Both industrial and residential users are leveraging smart grid technologies to cut costs, improve energy efficiency, and support sustainability initiatives.
Challenges & Opportunities
Challenges
-
High upfront infrastructure investment requirements.
-
Compatibility issues between legacy systems and new technologies.
-
Increased exposure to cyberattacks with digital grid adoption.
Opportunities
-
Expanding integration of renewable energy sources opens new revenue streams.
-
Growth in EV adoption and smart homes creates new avenues for grid innovation.
-
AI-powered analytics for grid operations present opportunities to improve efficiency and cost savings.
Future Outlook
Key growth will come from distributed energy resource integration, AI-driven grid intelligence, and wider deployment of IoT-enabled smart meters. Backed by favorable regulations, rising global power needs, and ongoing digital transformation, smart grids will remain a cornerstone of the future energy landscape.
Contact Us for a Detailed Overview: Cervicorn Consulting