Waste to Energy Market Overview
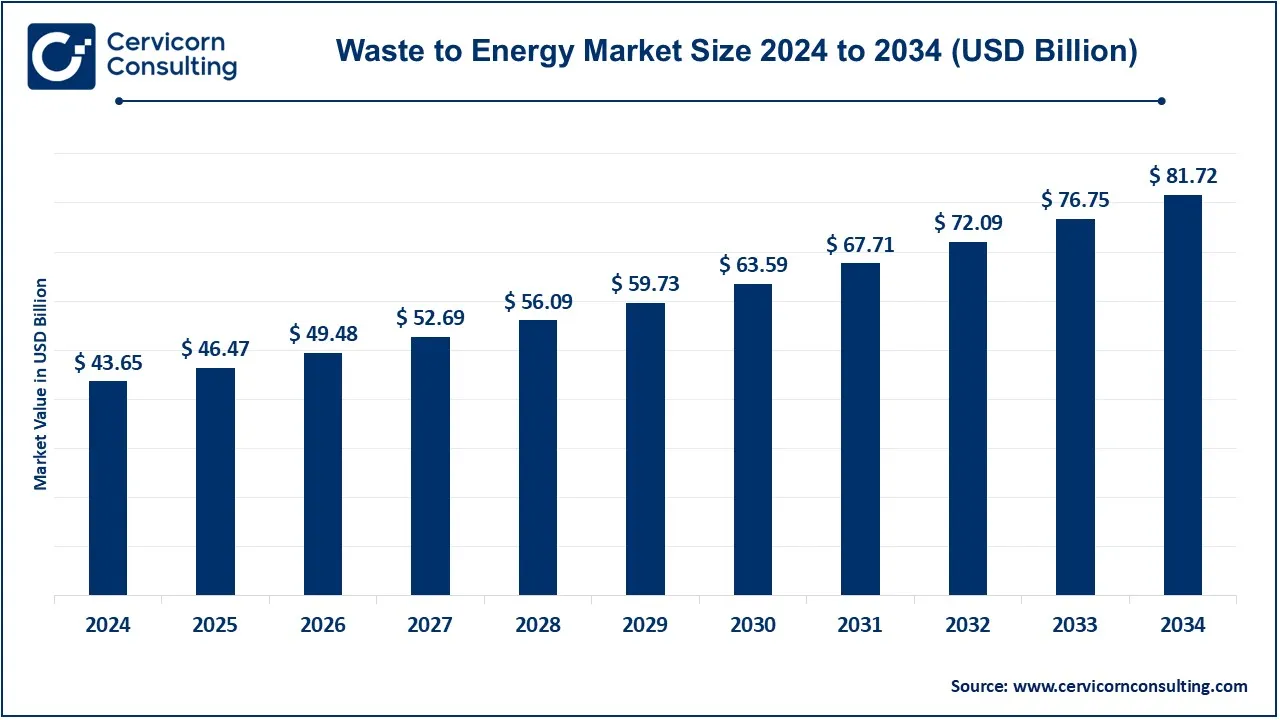
The global waste to energy market is rapidly emerging as a key solution for sustainable waste management and renewable energy production. The market was valued at USD 43.65 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 81.72 billion by 2034, reflecting a CAGR of 6.47% from 2025 to 2034. The market revolves around transforming municipal, industrial, and non-recyclable waste into usable energy forms such as electricity, heat, and fuel through technologies like incineration, anaerobic digestion, pyrolysis, and gasification. WtE initiatives not only curb landfill dependency but also reduce greenhouse gas emissions while promoting circular economy practices.
Key Market Trends
Several technological, regulatory, and operational trends are shaping the WtE industry globally:
-
Technological Innovations in Waste Processing
Advanced solutions including AI-driven waste sorting, enhanced gasification methods, and carbon capture systems are significantly improving operational efficiency in WtE plants. AI-based sorting, for instance, enhances the segregation of recyclable and non-recyclable materials, optimizing energy recovery and reducing operational costs. -
Integration with Circular Economy Models
Many companies are aligning WtE operations with circular economy principles, focusing on resource recovery and minimizing waste. Leading players like Veolia and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries are combining energy recovery with recycling and material recovery to maximize sustainability outcomes. -
Government Regulations and Incentives
Increasingly stringent environmental policies and renewable energy mandates are accelerating WtE adoption. Initiatives such as the EU Circular Economy Action Plan and the U.S. Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) are driving investment in WtE technologies and landfill gas-to-energy projects. -
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
Collaboration between governments and private enterprises is fostering the development of WtE projects, especially in emerging economies. Countries like India and Brazil are leveraging PPP models to finance and operate large-scale facilities efficiently. -
Focus on Decarbonization and Sustainability
The global drive toward decarbonization is positioning WtE as a vital contributor to reducing landfill methane emissions and replacing fossil fuels. Companies such as Hitachi Zosen and A2A SpA are deploying low-emission, high-efficiency incineration systems to meet environmental goals.
Market Drivers
Key factors fueling the growth of the WtE market include:
-
Rising Global Waste Volumes: Rapid urbanization and industrialization are generating vast amounts of municipal and industrial waste. Cities in China and India alone produce hundreds of millions of tons annually, spurring investment in WtE projects.
-
Technological Advancements: Innovations in gasification, pyrolysis, anaerobic digestion, and flue gas treatment are enhancing energy efficiency, lowering costs, and improving the economic viability of WtE plants.
-
Government Initiatives: National sustainability policies, subsidies, and carbon credits are incentivizing WtE adoption. Examples include the Sharjah WtE Plant in UAE and India’s Swachh Bharat Mission promoting WtE infrastructure.
-
Rising Demand for Renewable Energy: WtE complements other renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydro, supporting regional energy grids and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
-
Economic Viability and Employment Generation: WtE projects create jobs in engineering, operations, and maintenance, while generating revenue from energy production.
Impact of Trends and Drivers
The interplay of trends and drivers is influencing the market across applications, technologies, and regions:
-
Regional Adoption: Europe leads in integrating WtE with district heating and recycling systems, Asia-Pacific is experiencing rapid large-scale plant construction, and North America emphasizes landfill gas-to-energy projects.
-
Technology Segments: While incineration remains dominant, anaerobic digestion and gasification are gaining traction due to lower emissions and higher energy recovery efficiency.
-
Applications: Municipal solid waste (MSW) continues to dominate, followed by industrial waste, driven by stricter waste regulations and urban growth.
-
Corporate Strategy: Companies are leveraging technology, PPPs, and sustainability initiatives to expand market share and capitalize on high-growth opportunities.
Challenges & Opportunities
Challenges:
-
High capital costs for large-scale WtE facilities.
-
Compliance with stringent emission and environmental standards.
-
Public resistance due to environmental and health concerns.
Opportunities:
-
Expansion in emerging economies experiencing rapid urbanization.
-
Development of hybrid WtE technologies integrating recycling, biofuels, and energy storage.
-
Increased adoption of digital waste management and smart plant technologies to improve efficiency.
Future Outlook
The Waste-to-Energy market is projected to maintain strong growth, driven by increasing waste volumes, renewable energy demand, and technological innovations. With emerging trends such as AI-powered sorting, carbon capture, and circular economy integration further boosting efficiency and sustainability. As governments, industries, and communities focus on sustainable waste management and energy security, WtE is poised to play a pivotal role in the global green energy transition.