Power Electronics Market Overview
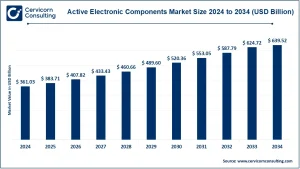
The global power electronics market is a cornerstone of modern energy management and electrification, encompassing technologies that control, convert, and optimize electrical power for diverse applications, including electric vehicles (EVs), industrial automation, and renewable energy systems. In 2024, the market is estimated at around USD 40.65 billion and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.56%, reaching nearly USD 69.8 billion by 2034. Core segments include power semiconductors, inverters, converters, motor drives, and power modules, which are widely deployed across automotive, industrial, renewable energy, and consumer electronics sectors (Cervicorn Consulting).
Key Market Trends
1. Wide-Bandgap Semiconductor Adoption (SiC & GaN)
The shift from traditional silicon devices to wide-bandgap semiconductors like silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN) is enabling smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient power devices. Automakers increasingly integrate SiC-based traction inverters in EVs, facilitating faster charging and improved energy efficiency.
2. Electrification of Transportation
Rising adoption of electric and extended-range vehicles (EVs & EREVs), e-buses, and commercial fleets is boosting demand for high-performance power electronics. Leading EV manufacturers such as Tesla, BYD, and Volkswagen deploy inverters, DC-DC converters, and onboard chargers from companies like Infineon and STMicroelectronics.
3. Integration of Renewable Energy Systems
Power electronics systems, including PV inverters, wind converters, and storage inverters, are witnessing higher adoption due to government-led solar, wind, and energy storage initiatives. Smart inverters now also provide grid support functions such as frequency regulation and reactive power management.
4. Industrial Automation & Smart Manufacturing
The rise of automated factories and robotics drives demand for energy-efficient variable frequency drives (VFDs), industrial motor controllers, and power modules, improving operational flexibility and reducing energy consumption.
5. Regulatory Push for Energy Efficiency
Governments are enforcing stricter efficiency standards globally, prompting replacement and upgrade cycles for industrial, commercial, and residential power electronics. Programs like India’s Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) for EV components and the EU Green Transition incentivize local production of energy-efficient solutions.
Market Drivers
Rising EV & EREV Adoption
Global EV sales are growing at double-digit rates, directly increasing demand for traction inverters, DC-DC converters, and onboard chargers. In Europe and China, EV penetration is projected to exceed 30% by 2030, further stimulating semiconductor demand.
Renewable Energy Expansion
Increasing solar and wind installations, particularly across Europe, Asia-Pacific, and North America, are driving investment in advanced inverters and storage converters. The global renewable energy market is projected to reach USD 1.5 trillion by 2030, supporting the growth of power electronics.
Technological Advancements
Innovations in wide-bandgap semiconductors, intelligent power modules, and integrated power ICs are improving efficiency, reducing device size, and accelerating deployment across EVs, industrial automation, and telecom infrastructure.
Government Initiatives and Policy Support
Regulatory measures, such as the U.S. CHIPS Act, EU semiconductor strategies, and India’s PLI scheme, promote domestic manufacturing of SiC/GaN devices, converters, and EV inverters, fueling market expansion.
Industrial Electrification & Smart Infrastructure
Rapid adoption of 5G networks, smart grids, and industrial automation increases demand for high-density power conversion systems, benefiting multiple market segments.
Impact of Trends and Drivers
-
Automotive: Adoption of EVs and hybrid vehicles increases the need for efficient SiC inverters, DC-DC converters, and chargers.
-
Renewables: Smart inverters enhance grid stability and optimize energy storage integration, especially in Europe and North America.
-
Industrial Automation: Use of wide-bandgap semiconductors improves energy efficiency, reduces operating costs, and enables compact designs for robotics and smart factories.
-
Telecom & Data Centers: High-density power conversion requirements for 5G infrastructure and cloud systems drive demand for advanced modules and power ICs.
Challenges & Opportunities
Challenges:
-
High initial cost of wide-bandgap devices and modules.
-
Supply chain constraints for SiC and GaN wafers.
-
Rapid technological evolution requiring ongoing R&D investment.
Opportunities:
-
Expansion into emerging EV and renewable energy markets.
-
Development of next-generation intelligent power modules and ICs.
-
Strategic partnerships for localized semiconductor manufacturing to leverage government incentives.
Future Outlook
The power electronics market is projected to experience robust growth, with a CAGR of 5.56% from 2025 to 2034, reaching an estimated USD 69.8 billion by 2034. Trends such as the electrification of transportation, wide-bandgap semiconductor adoption, smart industrial automation, and integration of renewable energy systems are expected to reshape market dynamics. Companies investing in SiC/GaN technologies, expanding manufacturing capacity, and aligning with government initiatives will likely secure a competitive edge in this rapidly evolving market.