Market Overview
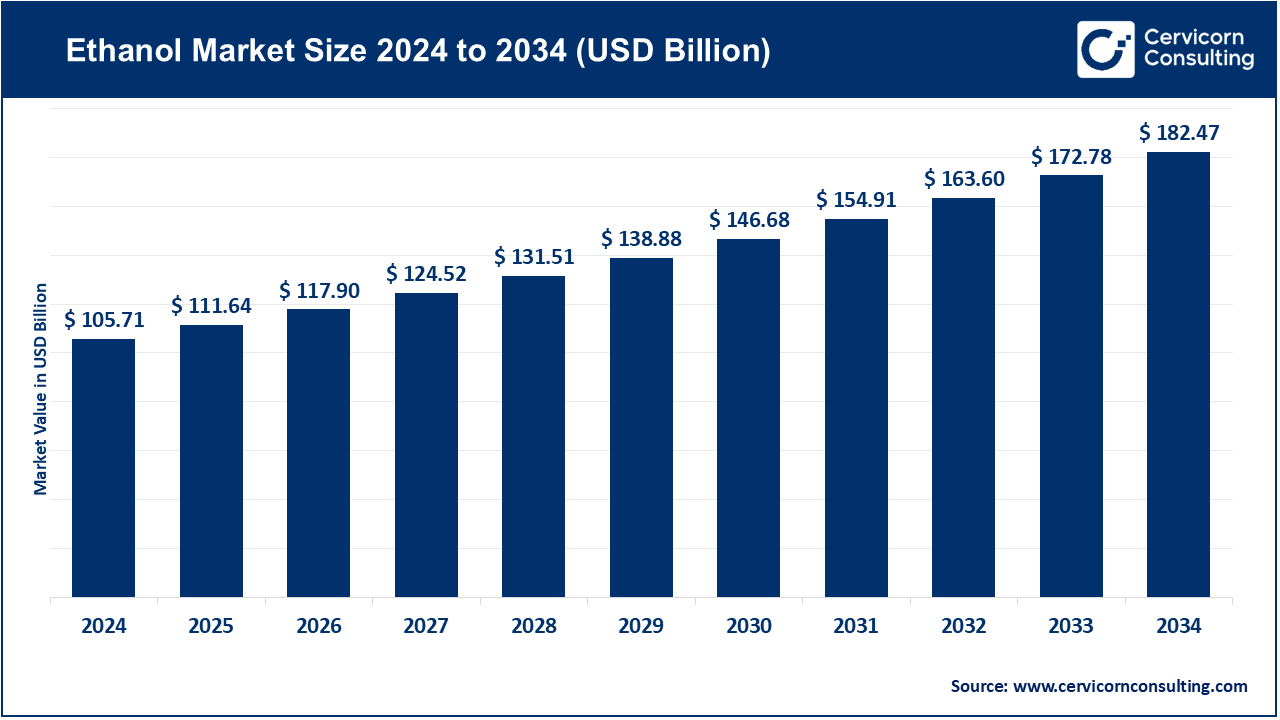
The global ethanol market has become a pivotal element in the clean energy transition, fueled by growing environmental concerns, increased biofuel adoption, and government policies supporting renewable alternatives to fossil fuels. As per Cervicorn Consulting, the market was valued at roughly USD 114.02 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 173.88 billion by 2034, representing a CAGR of 4.3% over the forecast period (2024–2034). Ethanol, primarily produced via the fermentation of sugarcane, corn, and other biomass sources, is widely used as a fuel additive to lower carbon emissions and improve engine performance.
The industry’s growth is bolstered by the worldwide shift toward sustainable energy policies, stricter blending mandates like E10 and E15, and rising demand for bio-based industrial products. North America leads the ethanol market, primarily due to strong production capabilities in the U.S., while regions such as Brazil, Europe, and Asia-Pacific demonstrate considerable growth potential.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2799
Key Market Trends
The ethanol sector is rapidly evolving, driven by technological innovations, changing regulations, and shifts in consumer and industrial preferences. Key trends include:
-
Advancements in Second-Generation (2G) Ethanol
Second-generation ethanol, derived from non-food biomass like agricultural residues, lignocellulosic material, and municipal waste, is gaining traction. This approach addresses the food-versus-fuel debate and enhances carbon efficiency. Companies such as Praj Industries and Raízen S.A. are leveraging advanced enzymes and cellulosic processes, improving yield efficiency by 20–25%. -
Strengthening Ethanol Blending Mandates
Governments worldwide are expanding ethanol blending programs to cut greenhouse gas emissions and reduce reliance on petroleum. Examples include the U.S. Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS), India’s Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) program targeting E20 by 2025–26, and Brazil’s Proálcool initiative, which continues to promote ethanol as a mainstream transport fuel. -
Expanding Bio-Based Industrial Applications
Ethanol’s role extends beyond fuel, with growing applications in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and industrial solvents. The shift toward green chemistry is encouraging producers to explore bioplastics and bio-based chemical intermediates, creating new revenue streams. -
Integration of Carbon Capture and Circular Bioeconomy
Leading firms like ADM and Green Plains Inc. are investing in carbon capture and storage (CCS) to achieve carbon-negative ethanol production. Circular economy models, which recycle waste into energy, are also being adopted, enhancing both profitability and sustainability. -
Strategic Partnerships and Global Collaboration
Joint ventures between energy majors, biotech firms, and governments are driving innovation. BP and Shell are expanding biofuel portfolios through collaborations, while Petrobras explores co-processing bioethanol with fossil fuels. These partnerships improve supply chain efficiency and accelerate technology adoption.
Market Drivers
Several factors are fueling global ethanol market growth:
-
Rising Demand for Sustainable Fuels
Increasing climate awareness and decarbonization efforts are key drivers. Ethanol produces 30–50% fewer greenhouse gas emissions than gasoline, making it critical for sustainable transport. The International Energy Agency (IEA) projects that biofuels, including ethanol, could meet up to 20% of global transport fuel demand by 2040. -
Government Policies and Incentives
Supportive policies and subsidies are promoting ethanol adoption. Countries such as the U.S., Brazil, India, and members of the EU have implemented blending mandates, tax incentives, and infrastructure funding. Initiatives like the U.S. Department of Energy’s Bioenergy Technologies Office (BETO) and India’s National Biofuel Policy (2018) exemplify this trend. -
Technological Innovations in Production
Improvements in feedstock processing, fermentation, and enzyme technologies have lowered production costs and increased efficiency. Advanced fermentation microbes and continuous distillation systems have shortened production cycles and boosted yields. -
Diversification Across Automotive and Industrial Uses
Ethanol’s versatility allows its use in flex-fuel vehicles, industrial solvents, personal care products, and disinfectants. The post-pandemic surge in ethanol-based sanitizers and industrial products has expanded market demand, particularly in developing regions. -
Global Push for Energy Independence
High crude oil prices and geopolitical tensions are prompting countries to enhance domestic biofuel production. Ethanol offers a cost-effective, locally sourced alternative that reduces import dependency, especially in emerging markets like India and Indonesia.
Impact of Trends and Drivers
Regional Impact:
-
North America: Dominates production, led by abundant U.S. corn supply and government incentives.
-
Brazil: Leverages low-carbon sugarcane ethanol.
-
Asia-Pacific: India and China are expanding capacity through blending mandates and agricultural innovations.
Application Impact:
-
Transportation: Accounts for over 70% of demand.
-
Industrial & Chemical: Growing rapidly, expected CAGR above 5% (2024–2034).
-
Pharmaceutical & Cosmetics: Increasing adoption as a sustainable solvent, boosting non-fuel demand.
Corporate Impact:
Leading players like ADM, POET LLC, Valero Energy, and Praj Industries are investing in next-gen ethanol, carbon reduction initiatives, and integrated biorefineries to strengthen competitiveness.
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges:
-
Feedstock Price Volatility: Dependency on corn and sugarcane exposes producers to price swings.
-
Infrastructure Limitations: Inadequate storage and blending facilities hinder adoption in developing regions.
-
Competition from EVs: Electric vehicle growth may moderate long-term fuel ethanol demand.
Opportunities:
-
Second- and Third-Generation Ethanol: Sustainable, waste-based production offers growth potential.
-
Emerging Markets: Industrialization and renewable policies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America provide new avenues.
-
Carbon Markets: Participation in carbon credit and low-carbon fuel standard programs can generate additional revenue.
Future Outlook
The ethanol market is set for steady growth, driven by sustainability policies, renewable fuel adoption, and advanced biofuel technologies. Projected to expand from USD 114.02 billion in 2024 to USD 173.88 billion by 2034 at a CAGR of 4.3%, the market will likely see:
-
Commercialization of cellulosic ethanol and multi-feedstock biorefineries.
-
Increased collaboration between oil majors and biofuel companies.
-
Digitalization and automation in production plants for improved efficiency and sustainability.
As governments continue to emphasize decarbonization and energy transitions accelerate, ethanol will remain a cornerstone of the global net-zero transportation agenda and a key driver of the bio-based economy.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us