Market Overview
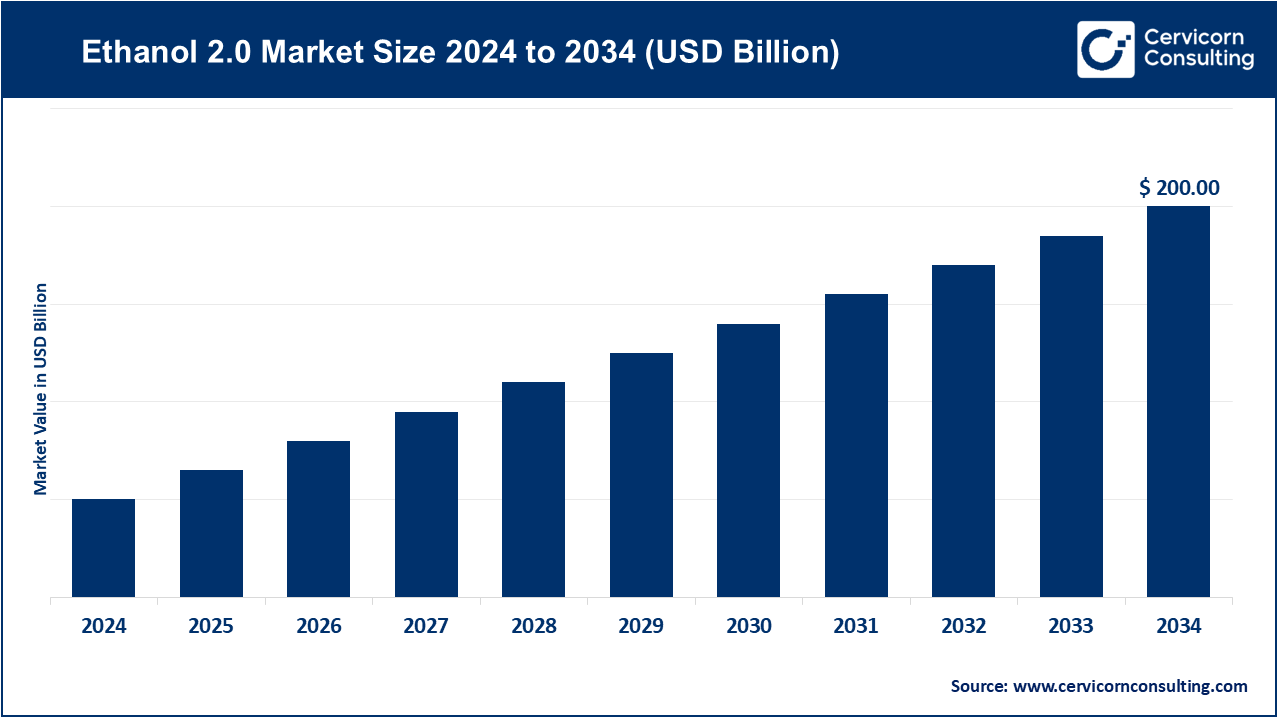
The global Ethanol 2.0 market is shaping the future of biofuels, emphasizing sustainability, circularity, and deep decarbonization. Industry estimates suggest that the market was valued at around USD 120 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to nearly USD 200 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of approximately 6% during 2025–2034. This expansion is fueled by increased investments in advanced biofuel technologies, global moves toward carbon neutrality, and the growing use of non-food feedstocks such as agricultural residues, forestry waste, and industrial by-products.
Ethanol 2.0, or second-generation (2G) ethanol, overcomes the limitations of conventional ethanol production by utilizing lignocellulosic biomass rather than food crops like corn or sugarcane. This approach addresses the “food vs. fuel” debate and significantly reduces greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, positioning Ethanol 2.0 as a cornerstone of sustainable energy systems. With governments enforcing renewable energy mandates and corporations committing to net-zero goals, the market is poised for transformative growth.
Get a Free Sample: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2798
Key Market Trends
1. Advanced Feedstock and Conversion Technologies
The ethanol sector is being transformed by innovations in biomass conversion. New pretreatment methods, enzyme breakthroughs, and improved fermentation techniques are enhancing yield and cost efficiency. Companies such as POET LLC and Archer Daniels Midland (ADM) are leveraging enzyme-based hydrolysis and microbial fermentation to efficiently convert agricultural residues like corn stover and wheat straw into ethanol. Integrated biorefinery models that co-produce bioethanol, biogas, and biochemicals are further improving operational sustainability and profitability.
2. Supportive Government Policies
Global regulatory frameworks are driving next-generation ethanol adoption. Programs like the U.S. Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS), EU Renewable Energy Directive (RED III), and India’s National Biofuel Policy are accelerating production and infrastructure growth. India’s E20 blending target for 2025–26 and incentives for residue-based ethanol plants are boosting local production while attracting private investment and international partnerships.
3. Decarbonization and Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF)
Ethanol 2.0 is increasingly being integrated into SAF supply chains, helping reduce aviation-related CO₂ emissions (~2.5% of global emissions). Companies such as LanzaJet and Raízen are pioneering ethanol-to-jet (EtJ) technologies, converting ethanol into drop-in jet fuel to help airlines comply with CORSIA regulations. This trend expands ethanol’s application beyond traditional automotive fuels.
4. Carbon Capture and Renewable Integration
Bioethanol facilities are adopting carbon capture and storage (CCS) and renewable energy sources to minimize emissions. Firms like Valero Energy Corporation and Green Plains Inc. are co-locating ethanol plants with renewable hydrogen and CCS systems, reducing carbon intensity and qualifying for low-carbon fuel credits in markets such as California and the EU.
5. Digitalization and Smart Bioenergy Operations
Technological adoption, including AI, IoT, and analytics, is optimizing ethanol production. Real-time monitoring of fermentation, predictive analytics for feedstock logistics, and maintenance optimization are helping producers like Cargill and BP Biofuels increase efficiency while navigating stringent regulatory environments.
Market Drivers
1. Rising Demand for Low-Carbon Fuels
The global push toward net-zero emissions by 2050 is increasing demand for sustainable biofuels. Ethanol 2.0, which delivers 60–90% lower GHG emissions than fossil fuels, is gaining traction. Government fuel-blending mandates, including E15 and E20 targets, ensure steady market growth. Ethanol’s role in SAF and bio-based chemicals further diversifies its applications alongside the expanding EV market.
2. Government Incentives and Blending Mandates
Financial incentives like carbon credits, tax rebates, and biofuel grants are attracting investments in advanced ethanol projects. Initiatives such as the U.S. DOE’s BETO and Brazil’s RenovaBio program are enabling large-scale 2G ethanol deployment while fostering partnerships with energy and technology companies.
3. Feedstock Diversification and Rural Development
By utilizing agricultural residues and municipal waste, Ethanol 2.0 promotes rural income and waste reduction. Farmers benefit from selling crop residues, while local communities gain employment through biomass collection and biorefinery operations, aligning with UN SDGs for sustainable consumption and production.
4. Technological Innovations Lowering Production Costs
Advances in enzyme catalysis, thermochemical conversion, and genetic engineering have reduced ethanol 2.0 production costs by 25–30% over the past decade. Commercial-scale cellulosic ethanol and synthetic biology fermentation are enabling scalability and consistent output, particularly in the U.S. and Europe.
5. Corporate Sustainability Commitments
Major energy and consumer goods companies, including BP, Shell, and TotalEnergies, are investing in Ethanol 2.0 to meet carbon offset goals. Global consumer brands are also exploring ethanol-derived bio-plastics and solvents, extending applications beyond energy into the broader bioeconomy.
Regional Impact
-
North America: Leads in technology and infrastructure with regulatory clarity and established feedstock supply chains.
-
Latin America: Brazil benefits from sugarcane expertise and government support via RenovaBio.
-
Europe: Focuses on SAF adoption and industrial decarbonization in line with Fit-for-55 goals.
-
Asia-Pacific: India and China are emerging markets driven by policy support, biomass availability, and energy security objectives.
Ethanol 2.0 is also influencing green hydrogen production and chemical feedstocks, enhancing synergies between renewable energy and industrial decarbonization.
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges:
-
High capital costs for biorefineries
-
Complex feedstock logistics, especially in developing regions
-
Policy inconsistencies and volatile oil prices
Opportunities:
-
Integration with CCS and renewable systems
-
Expansion into aviation and marine fuel markets
-
Accelerated technology commercialization through collaborative R&D
Future Outlook
By 2034, the Ethanol 2.0 market is expected to reach USD 200 billion, reflecting a CAGR of nearly 6%. The next decade will see wider commercialization of cellulosic ethanol, ethanol-based SAF adoption, and integration with carbon management and renewable hydrogen systems. Leading companies such as ADM, POET LLC, Valero Energy Corporation, Cargill, and Green Plains Inc. will drive this transformation through innovation, partnerships, and policy-aligned investments.
For Detailed Market Insights, Contact Us: https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us