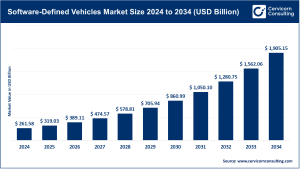
Market Overview
The global fuel cell market was valued at around USD 8.65 billion in 2024 and is forecast to grow at a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 18.90% during the forecast timeline, surpassing USD 48.85 billion by 2034.
Momentum in the fuel cell market is accelerating as governments and industries worldwide intensify efforts to shift toward low-carbon and zero-emission energy systems. Fuel cells produce electricity through an electrochemical process, delivering high efficiency, minimal emissions, and dependable power for stationary, portable, and transportation-based applications.
With its current multi-billion-dollar valuation, the fuel cell market is poised for consistent expansion, driven by increased investments in clean energy technologies, the advancement of the hydrogen economy, and supportive regulatory frameworks. The market covers a broad spectrum of technologies, including proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs), solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), molten carbonate fuel cells (MCFCs), and others, catering to diverse end-use sectors such as automotive, power generation, industrial energy, and backup power solutions.
Get a Free Sample:
https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/sample/2653
Key Market Trends
1. Rising Adoption of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
A major trend shaping the fuel cell market is the growing deployment of hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs). Automakers are expanding their fuel cell offerings across passenger vehicles, buses, trucks, and commercial fleets. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions with well-developed hydrogen refueling infrastructure and strong policy support, positioning fuel cells as a compelling alternative to battery-electric technologies for long-range and heavy-duty mobility.
2. Increasing Deployment of Stationary Fuel Cell Systems
Stationary fuel cells are witnessing rising adoption for distributed power generation, backup power, and combined heat and power (CHP) applications. Sectors such as healthcare, data centers, manufacturing, and commercial buildings are increasingly turning to fuel cells to enhance energy reliability while lowering carbon emissions. This trend is reinforced by the growing need for decentralized and uninterrupted power supply.
3. Advancements in Fuel Cell Performance and Efficiency
Ongoing innovation in fuel cell stack architecture, catalysts, membranes, and system integration is improving efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Progress in PEM and SOFC technologies is enabling longer operational lifespans and higher performance levels, supporting broader commercial adoption across multiple industries.
4. Strengthening Government Support for Hydrogen Infrastructure
Governments across major economies are actively advancing hydrogen and fuel cell technologies through national hydrogen roadmaps, financial incentives, tax benefits, and demonstration projects. These initiatives are accelerating investments in hydrogen production, storage, and distribution infrastructure, creating a strong foundation for fuel cell market expansion.
5. Growing Industrial Demand for Clean Power Solutions
Industrial users are increasingly incorporating fuel cells into their decarbonization strategies. Fuel cells offer reliable, scalable, and low-emission power, making them an attractive option for manufacturing facilities and industrial campuses seeking to meet sustainability and emission-reduction goals.
Market Drivers
Rising Demand for Clean and Low-Emission Energy
The global emphasis on reducing greenhouse gas emissions remains the primary driver of fuel cell market growth. Fuel cells deliver electricity with negligible or zero harmful emissions, positioning them as a key technology in the global transition toward sustainable energy—particularly in transportation and power generation sectors.
Supportive Government Policies and Incentive Programs
Favorable regulatory environments and government funding initiatives are significantly accelerating fuel cell adoption. Investments in hydrogen infrastructure, fuel cell vehicle programs, and clean energy research are reducing entry barriers and encouraging increased participation from private sector players.
Technological Innovation and Cost Optimization
Continuous research and development efforts are lowering fuel cell system costs while improving operational efficiency. Breakthroughs in materials science, manufacturing techniques, and system integration are enhancing the commercial competitiveness of fuel cell technologies across various applications.
Growing Energy Security and Resilience Needs
Fuel cells support energy security by enabling on-site power generation and reducing reliance on centralized electricity grids. This factor is particularly important in regions experiencing grid instability, high energy costs, or frequent power disruptions.
Expansion of Hydrogen Production Capabilities
The rapid growth of green and low-carbon hydrogen production capacity is directly supporting fuel cell adoption. As hydrogen becomes more widely available and cost-competitive, fuel cells are increasingly viewed as a practical and scalable energy conversion solution.
Impact of Trends and Drivers on the Market
The combined influence of these trends and growth drivers is reshaping fuel cell deployment across industries and geographies. Transportation applications are benefiting significantly from government incentives and expanding hydrogen infrastructure, while stationary fuel cell systems are gaining traction in commercial and industrial environments prioritizing energy reliability. Regionally, countries with established hydrogen strategies and strong decarbonization commitments are experiencing faster adoption, while emerging markets are gradually entering the space through pilot projects and industrial use cases.
Challenges and Opportunities
Although the fuel cell market offers substantial growth potential, challenges remain, including high upfront costs, limited hydrogen refueling infrastructure, and supply chain constraints. However, these challenges also create opportunities for innovation in cost reduction, hydrogen storage solutions, and infrastructure development. Companies focusing on scalable manufacturing, strategic collaborations, and technological advancements are well positioned to capture emerging opportunities.
Future Outlook
The fuel cell market is expected to sustain strong growth throughout the forecast period, supported by continued government support, expanding hydrogen ecosystems, and rapid technological progress. The market is anticipated to maintain a high double-digit CAGR, achieving a significantly higher valuation over the next decade. Emerging use cases in heavy-duty transportation, industrial power generation, and distributed energy systems are expected to play a pivotal role in defining the future direction of the fuel cell industry.
To Get Detailed Overview, Contact Us:
https://www.cervicornconsulting.com/contact-us